Foreign Bribery in Ericsson
Por: Laura Paola Villa García | Posted on December 25, 2019

Facts: Who gave what to whom and why?
The Swedish telecommunications company Ericsson admitted conspiring with others to violate the provisions of the FCPA from 2000 to 2016 by participating in a scheme to pay bribes in five countries including China and Vietnam, falsify books and records and failing to implement internal controls. According to the United States Department of Justice, Ericsson paid bribes to government officials using consultants which were hired through sham contracts and paid in accordance to false invoices (International, 2019).
In China, the company paid tens of millions of dollars to consultants and a portion of the money was used to pay travel, gifts and entertainment to public officials. Also, from 2010 to 2016, Ericsson subsidiaries paid approximately 31.5 million dollars to third party providers in services not rendered mischaracterizing these payments in their books and records. In addition, the payments were made with the purpose of allowing the company to operate through third arty agents in China in contravention to Ericsson policies and procedures (International, 2019).
Between 2011 and 2013, the company promised a payment of 450,000 to request a consulting company a sales agent in Kuwait and then hired the company through a sham contract for services not rendered. The sales agent then gave insight information regarding a telecommunications tender. As a result, Ericsson was awarded with a 182 million telecommunications contract and the company made the 450,000 payment to the consulting company, which off course was incorrectly labeled in their books and records (International, 2019).
Between 2012 and 2015 Ericsson made USD $4.8 million and 45 million mischaracterized and improperly recorded payments to consulting firms in Vietnam and Indonesia, respectively.
After the investigation, the US Department of Justice came to the conclusion that Ericsson failed to disclose the seriousness of the violations of the FCPA in five countries involving of some of their high-level executives (International, 2019).
Law
United Nations Convention Against Corruption
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
Why the case is relevant?
This case is extremely relevant as Ericsson agreed to pay over USD$1 billion to the United States authorities, specifically to U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and the Department of Justice for violations to the FCPA, which is a sum even higher than what Walmart paid for the FCPA resolution (USD $282 million).
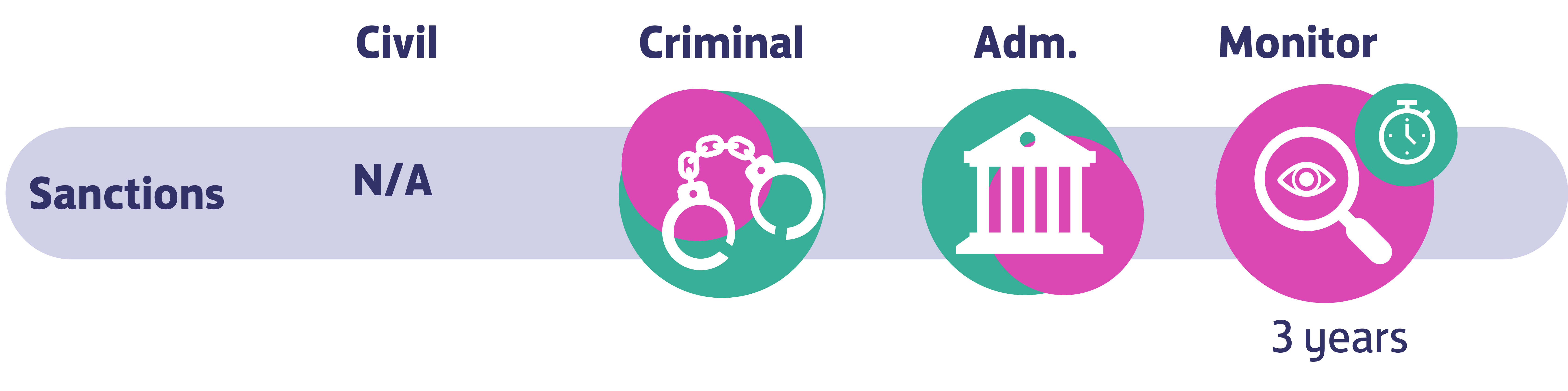
Also, the relevance lays in the fact that the US Department of Justice is going further to unveil cases of foreign bribery linked to various multinational companies that 1) operate in the United States; 2) issue securities in US Stock Exchange; or 3) are linked to transactions in the United States (International, 2019).
Lessons learned
Perhaps the biggest lesson we can learn from this case is that it is an indicator that the US government will not stop their investigations when it comes to foreign bribery. In addition, we can learn that in order to prevent corrupt practices, it is necessary to implement effective compliance systems and internal accounting controls in order to avoid bribes to be disguise in legal and legitimate payments (International, 2019).
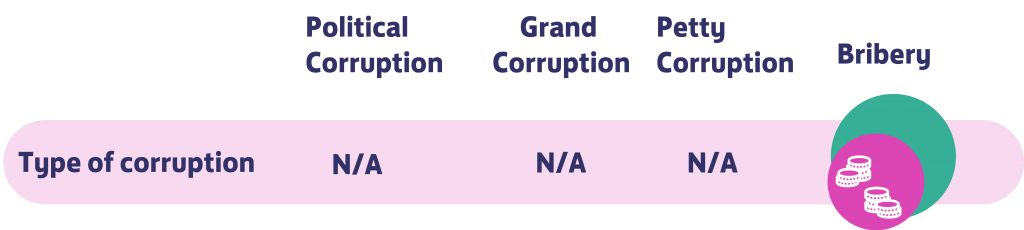
What type of corruption is it and what are the crimes involved?
The crimes involved in this case are mainly bribery, which consists in the “offering, promising, giving, accepting or soliciting of an advantage as an inducement for an action which is illegal, unethical or a breach of trust. Inducements can take the form of gifts, loans, fees, rewards or other advantage” (International, 2019) in this case, Ericcson pay consulting firms in order to pay the bribes to foreign public officials. In addition, Ericcson also mischaracterized payments and failed to implement internal accounting controls (International, 2019).
References (Harvard – Anglia)
Justice, T. U. S. D. o., 2019. The United States Department of Justice. [Online]
Available at: https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/ericsson-agrees-pay-over-1-billion-resolve-fcpa-case
International, T., 2019. Transparency International the global coalition against corruption. [Online]
Available at: https://www.transparency.org/en/glossary
